Ancient Egyptian Symbols
And Their Meanings
Symbols were used in Ancient Egypt to convey important cultural values and relay historical information about gods and kings.
These symbols appeared in all forms of artwork, jewellry, and architecture.
This page features some of the most common ancient symbols that were used by the Egyptians.
Egyptian symbols are popular due to their ornate detail and symbolic meaning.
Each symbol below also contains the meaning of the symbol.
Eye of Horus Symbol

The Eye of Horus is the ancient Egyptian symbol for the sun.
The Eye of Horus represents the all-seeing eye so named after Horus, the God of the Sky, who lost and eye during battle.
The Eye of Horus represents protection, royal power and good health.
Ankh Symbol

The ankh is a cross with a loop on the top. The ankh is the ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic character that symbolized eternal life.
Egyptians are strong believers in the afterlife and that the ankh helped protect them and helped them transition to life after death. Egyptian gods are often portrayed carrying it by its loop, or bearing one in each hand, arms crossed over their chest.
A God holding an ankh to someone's lips is considered to be an offering of "The Breath of Life".
The ankh symbol is a popular design choice for a tattoo which is often placed on the ankle or inside the wrist.
The Falcon Symbol

Egyptians associated the Falcon with the solar god Horus, one of the most famous gods of ancient Egypt and the son of Osiris and Isis. The falcon was symbolic of the rising sun in Egypt. The falcon was also sacred to Montu the god of war.
The falcon symbol represents vision, freedom and victory.
Egypt Air has adopted this symbol as their logo.
The Feather of Maat Symbol

The Feather of Maat symbol represents truth, justice, morality and balance.
It was a pharaoh's job to uphold Maat. When a pharaoh died, Maat was lost and the world was flung into chaos, only the coronation of a new pharaoh could restore Maat.
Egyptian Scarabs Symbol

The ancient Egyptians saw how these beetles (scarabs) lived and emerged from dry ground and used this as a metaphor for the entombing and resurrection of their mummies.
In this way the beetle became the Egyptian symbol for rebirth, the ability to be reborn.
The Lotus Flower Symbol

The lotus flower closes at night and then sinks underwater. In the morning it emerges and blooms again. Thus the flower became a natural symbol of the sun and creation.
The lotus was commonly used in art as a symbol of Upper Egypt. The lotus flower is also known as a symbol of rebirth, the renewal of life and the promise of everlasting life.
The Winged Sun Symbol
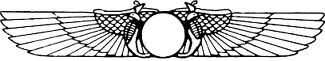
represents a solar eclipse, thus the reference solar disk. The wings are supposed to represent the sun's corona during this event. The winged sun is a symbol associated with divinity, royalty and power in the Ancient Near East (Egypt, Persia, etc.)
Sphinx Symbol

The sphinx is a mythical creature with a lion's body and human head.
The Sphinx is said to have guarded the entrance to the Greek city of Thebes, and to have asked a riddle of travellers to allow them passage. The exact riddle asked by the Sphinx was not specified by early tellers of the stories, and was not standardized as the one given below until late in Greek history.
The oldest known sphinx was found in Gobekli Tepe, Turkey dated 9,500 BC.
The Uraeus Symbol

The uraeus is a rearing cobra with a flared hood. Often worn on the forehead uraeus was a symbol of protection.
The uraeus was used as a symbol of sovereignty, royalty, deity, and divine authority in ancient Egypt.
The Uraeus is a symbol for the goddess Wadjet, who was one of the earliest Egyptian deities and who was often depicted as a cobra.
Djed Symbol

The djed is a pillar-like symbol in hieroglyphics representing stability. It is associated with Osiris, the Egyptian god of the afterlife, the underworld, and the dead. It is commonly understood to represent his spine.
It was also sometimes used to represent Osiris himself, often combined "with a pair of eyes between the crossbars and holding the crook and flail."
Was Symbol
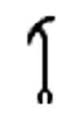
The Was scepter is a staff with the head of a canine at the top. This is a symbol of power and dominion. The Was scepter is carried by deities as a sign of their great power.
Egyptian Pyramid Symbol

One of the most recognised symbols of Egypt. These amazing stone monuments were built as tombs for the country's Pharaohs and their consorts during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods.
Flail and Crook

The Flail and Crook are symbols of royalty, majesty and dominion.
The flail is depicted alongside the "crook" as symbols of office for the crowned Egyptian Pharaoh. The flail symbolises the Pharaoh's role as provider of food for his people and the crook symbolises his role as the shepherd of his people. Both crook and flail also serve to link the Pharaoh with Osiris. Depictions of Anubis, the jackal-headed god of the embalming, also include the flail as an attribute.
Hedjet Symbol
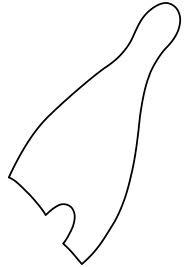
The White Crown. This was the crown of Upper Southern Egypt
